学会CI/CD
标准开发流程里,在之前,开发测试发布可能是三个人,由于DevOps的流行导致很多时候开发测试发布是一个人,于是衍生出了很多CI/CD平台。
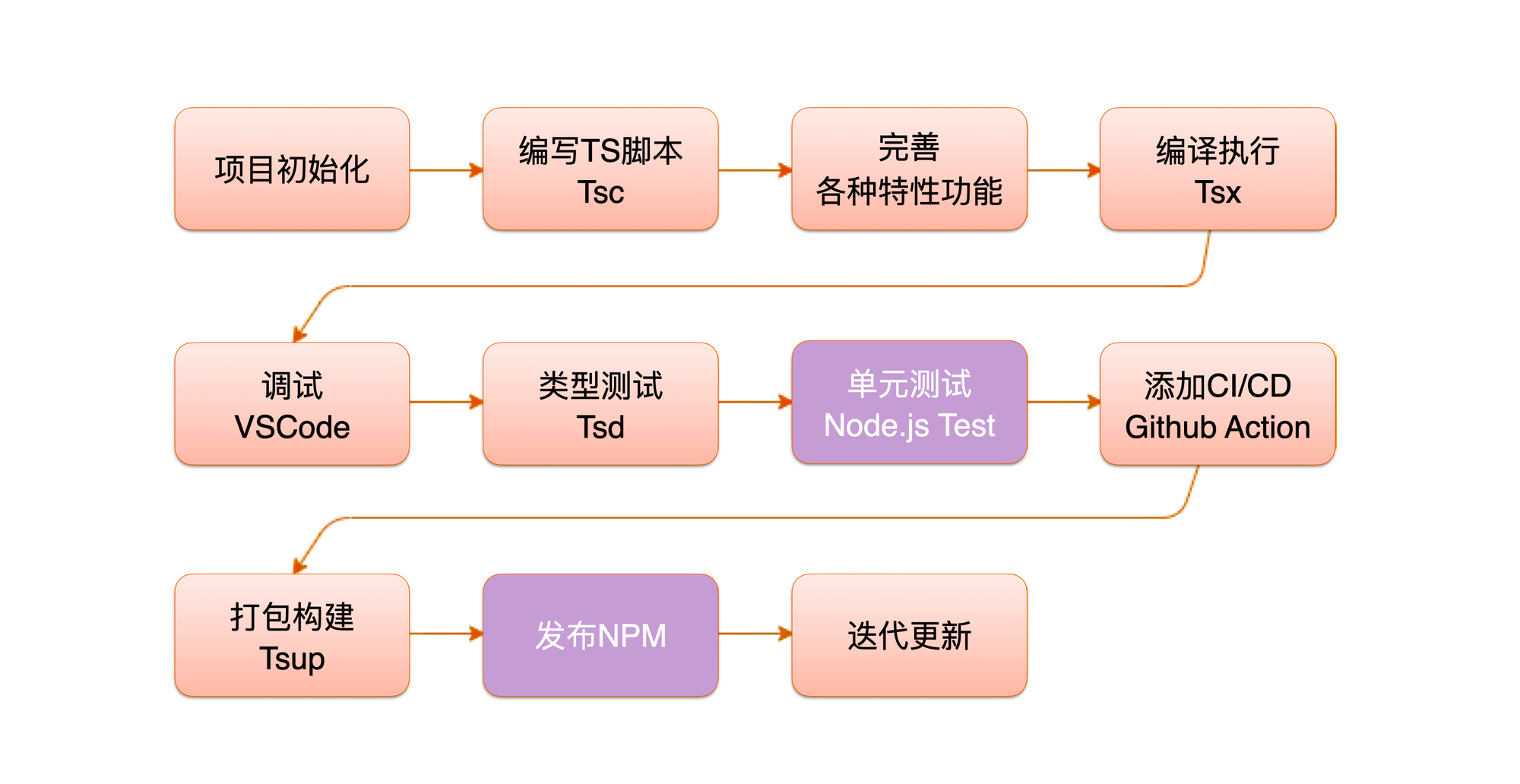
举个例子,以前我们发布npm模块,在本地执行npm publish即可。现在流行的方式是在代码merge到main分分支的时候触发CD,在github actions上直接发布。这在很大程度上更加便利,但也使得学习内容变多了。
下面我们就讲讲CI/CD
使用Github Actions
持续集成(Continuous Integration,CI)是一种软件开发实践,通过自动化构建、测试和部署过程,来确保代码的质量和稳定性。CI的目的是尽早发现和解决代码中的问题,以便快速交付高质量的软件。
在CI中,开发者将代码提交到版本控制系统中,然后自动触发构建、测试和部署过程。如果构建或测试失败,开发者会收到通知,以便及时修复问题。这样可以避免在部署时出现问题,并且可以提高开发效率和软件质量。
GitHub Actions(同类产品 CircleCI 、TravisCI)是GitHub提供的一种持续集成和部署工具,可以自动化构建、测试和部署GitHub仓库中的代码。它与GitHub紧密集成,可以通过简单的配置文件来定义工作流程,同时支持多种编程语言和操作系统。
使用GitHub Actions,开发者可以轻松地设置自动化构建和测试流程,以便在代码提交时自动运行。它还支持自定义环境变量、定时触发、通知和部署等功能,可以满足不同项目的需求。
总的来说,持续集成是一种重要的软件开发实践,可以提高软件质量和开发效率。GitHub Actions是一种方便、灵活的CI工具,可以帮助开发者自动化构建、测试和部署GitHub仓库中的代码。
$ cat .github/workflows/main.yml
name: Node.js CI
on: ["push", "pull_request"]
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Use Node.js
uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: "20.x"
- run: npm install
- run: npm test
- run: npm run test:coverage
- name: Upload coverage reports to Codecov
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v3
env:
CODECOV_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
with:
file: ./coverage/lcov.info
这里面顶一个2个任务
1、Use Node.js
2、Upload coverage reports to Codecov
查看actions
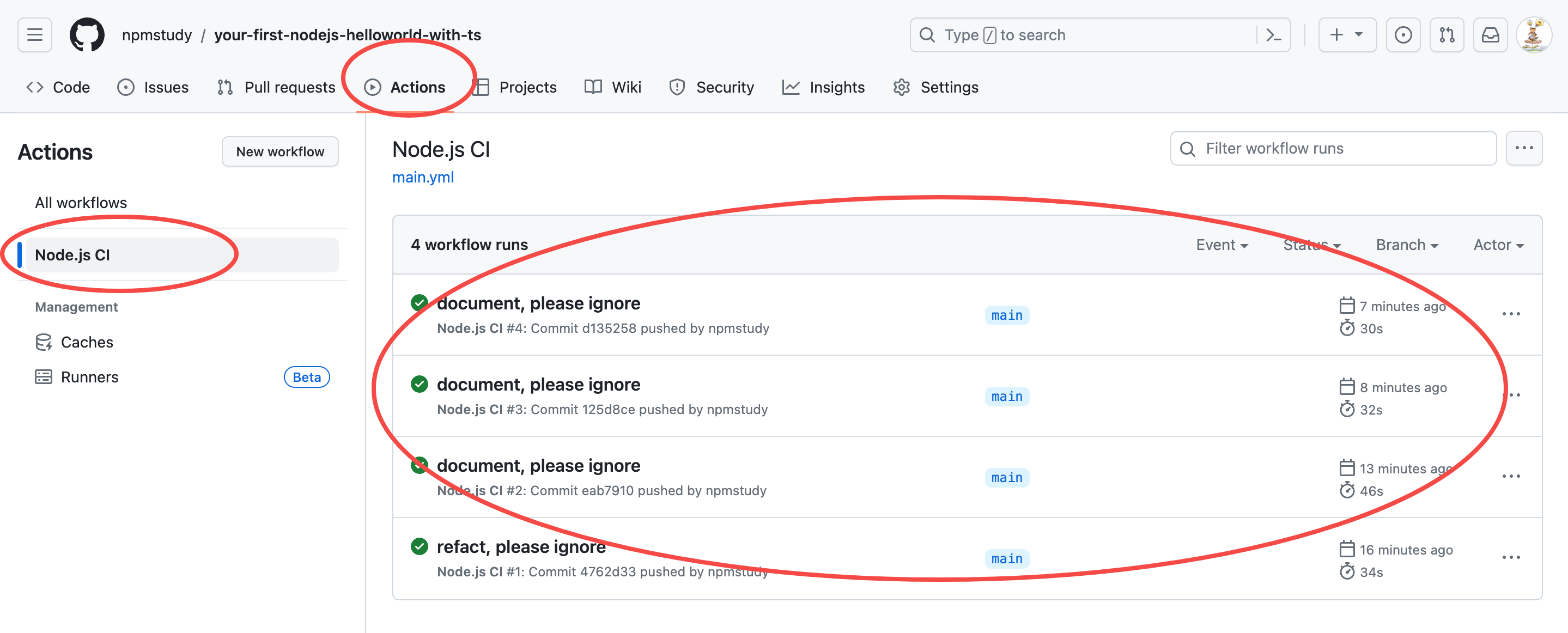
查看最近一次代码提交触发的ci记录
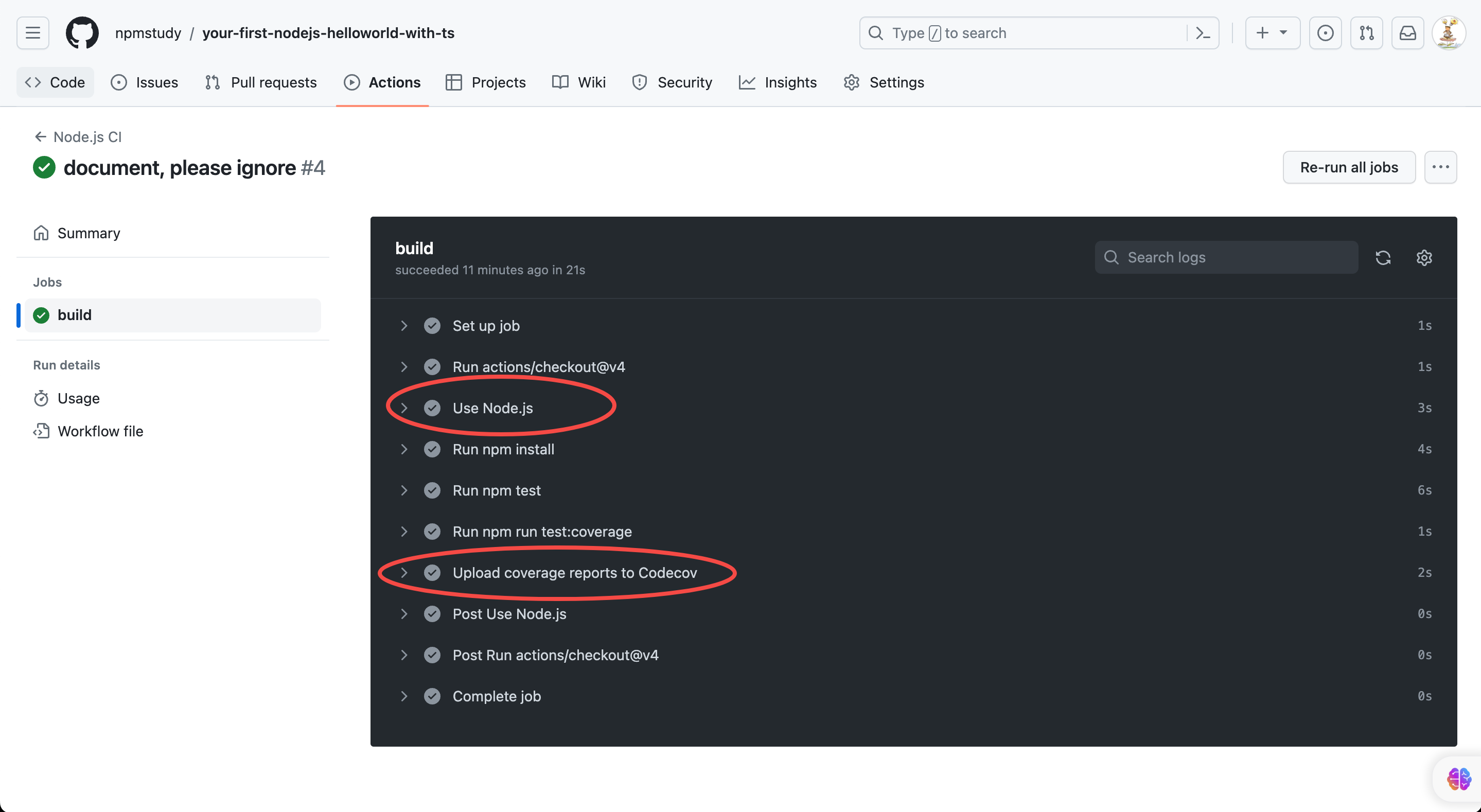
测试覆盖率
使用c8做测试覆盖率生成。
"scripts": {
"test:coverage": "c8 tsx --test test/*.ts",
}
增加配置.c8rc.json,注意配置中的reporter里的lcov是必须配置的。
{
"reporter": [
"lcov",
"text",
"html"
]
}
执行npm run test:coverage就可以生成对应的测试覆盖率文件了。
测试覆盖率会放在coverage目录下面,打开coverage/index.html文件。
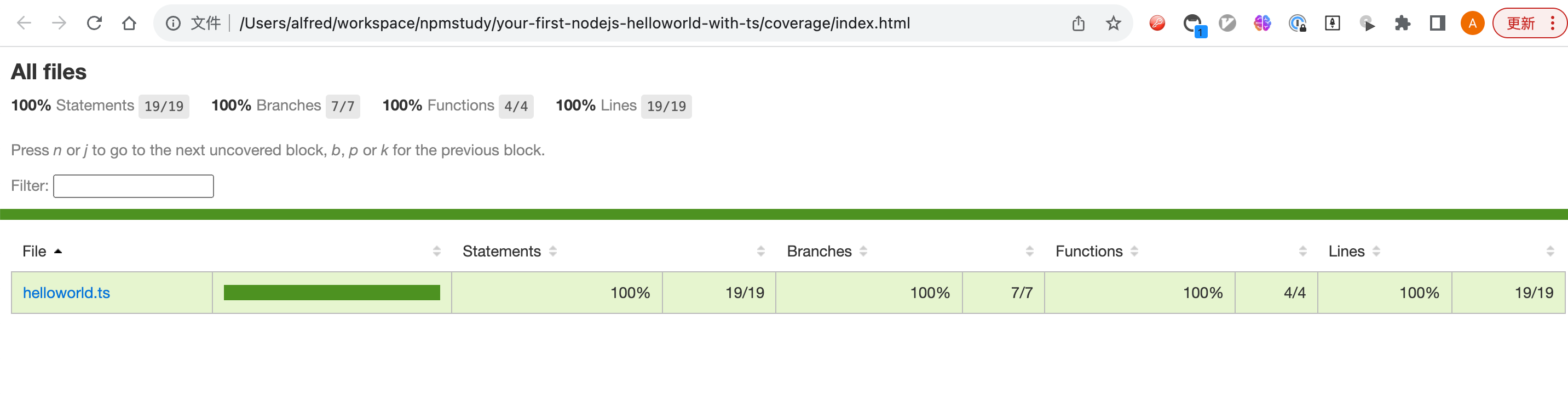
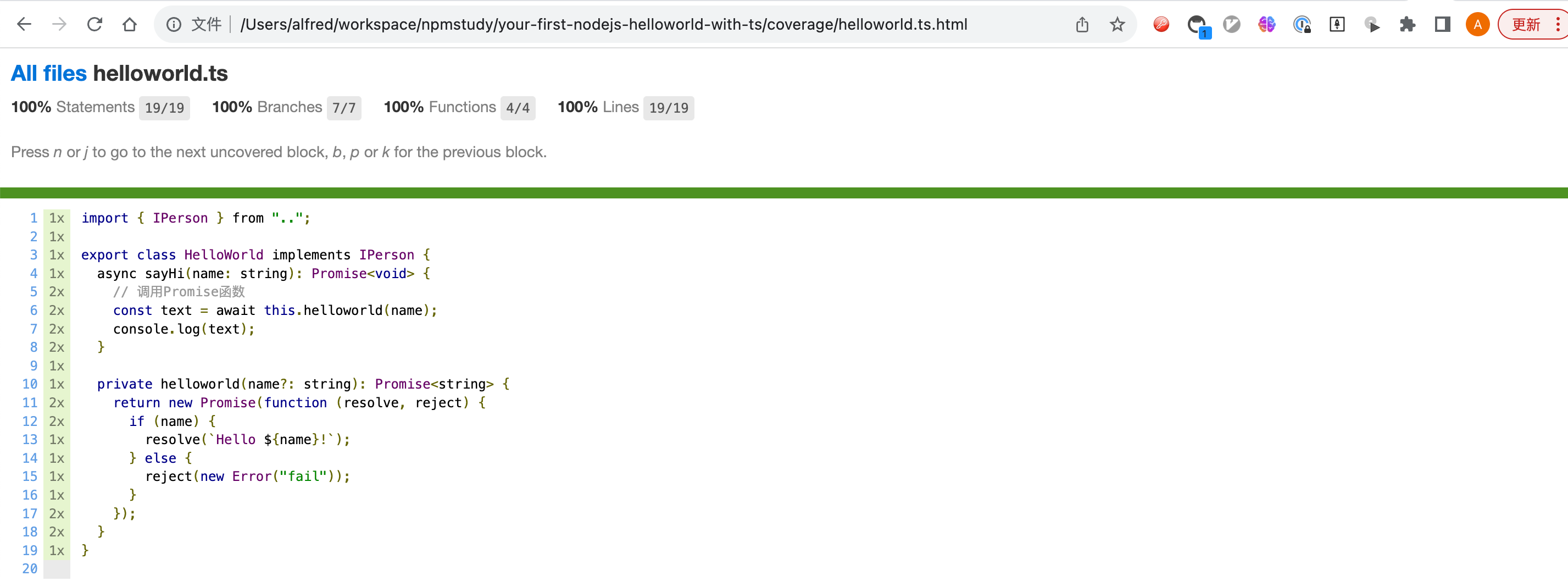
测试覆盖率是保证测试有效的必备手段。
还是以之前的代码举例
import { IPerson } from "..";
export class HelloWorld implements IPerson {
async sayHi(name: string): Promise<void> {
// 调用Promise函数
const text = await this.helloworld(name);
console.log(text);
}
private helloworld(name?: string): Promise<string> {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
if (name) {
resolve(`Hello ${name}!`);
} else {
reject(new Error("fail"));
}
});
}
}
如果只是测试sayHi,代码如下。
import { test, describe } from "node:test";
import assert from "node:assert";
import { HelloWorld } from "../src/helloworld";
import { IPerson } from "..";
describe("test suite", function () {
test("test if works correctly", async function (t) {
const log = t.mock.method(global.console, "log");
assert.strictEqual(log.mock.callCount(), 0);
// call hello world say method
const cli: IPerson = new HelloWorld();
await cli.sayHi("liangqi");
assert.strictEqual(log.mock.callCount(), 1);
});
});
此时查看测试覆盖率89.47%
$ npm run test:coverage
> your-first-nodejs-helloworld-with-ts@1.0.0 test:coverage
> c8 tsx --test test/*.ts
Hello liangqi!
▶ test suite
✔ test if works correctly (0.864584ms)
▶ test suite (1.637167ms)
ℹ tests 1
ℹ suites 1
ℹ pass 1
ℹ fail 0
ℹ cancelled 0
ℹ skipped 0
ℹ todo 0
ℹ duration_ms 158.421208
---------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
File | % Stmts | % Branch | % Funcs | % Lines | Uncovered Line #s
---------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
All files | 89.47 | 83.33 | 100 | 89.47 |
helloworld.ts | 89.47 | 83.33 | 100 | 89.47 | 15-16
---------------|---------|----------|---------|---------|-------------------
此时查看测试报告,具体如下
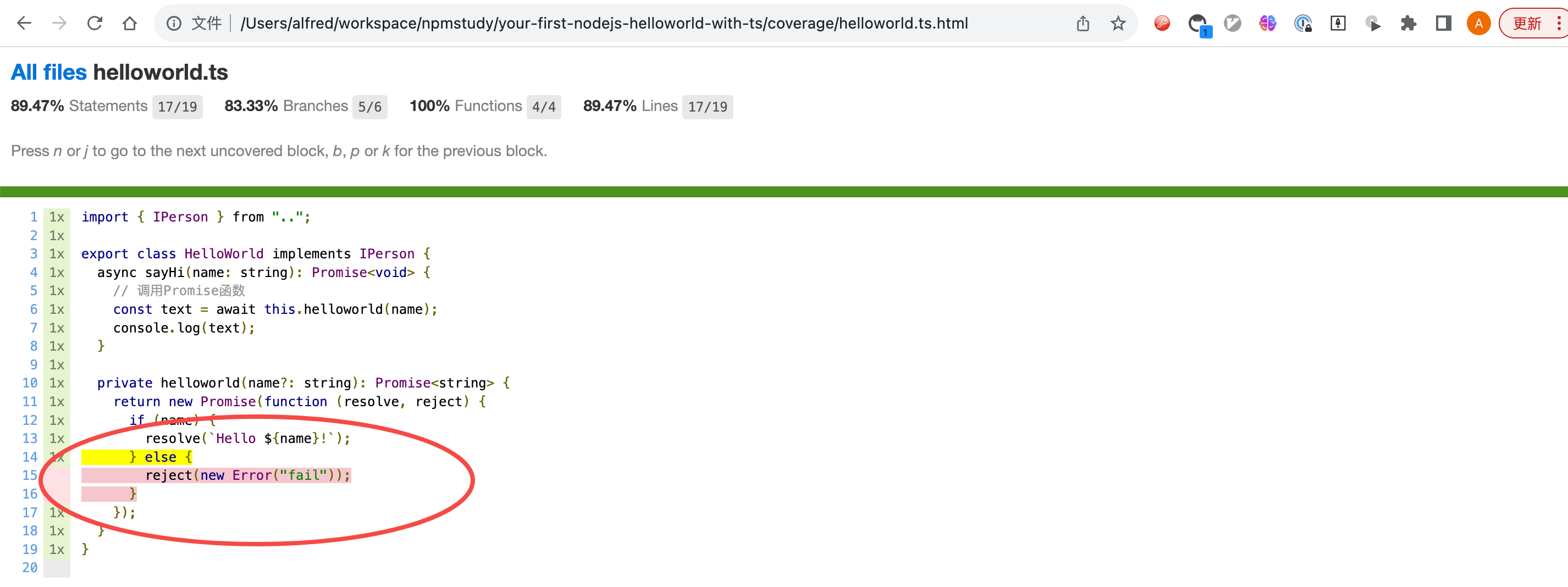
非常明显是helloworld中的else逻辑没有覆盖。
修改测试代码,增加下面的代码。
test("test if works incorrectly", async function () {
const cli: IPerson = new HelloWorld();
assert.rejects(async () => await cli.sayHi(), new Error("fail"));
});
在执行测试覆盖率脚本,此时就100%了。
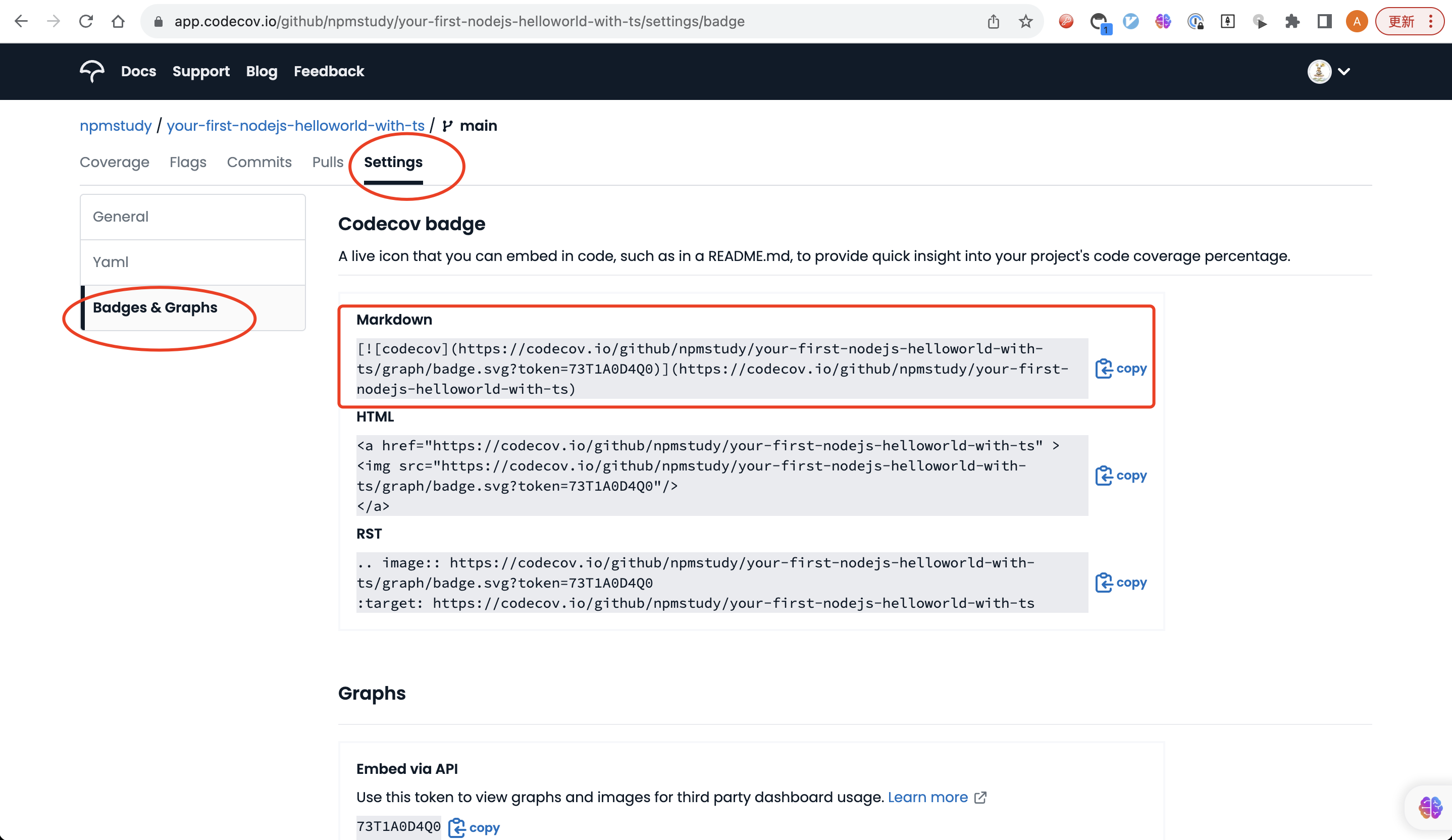
Badge
在README.md文件中的badge是一种徽章,通常用于展示项目的一些信息或状态。徽章可以显示项目的构建状态、测试覆盖率、版本号、许可证、支持的平台等等。这些徽章可以帮助读者快速了解项目的一些关键信息,同时也可以增加项目的可信度和吸引力。徽章通常是通过图像或链接的形式呈现在README.md文件中。
例如我们的项目README.md展示如下。
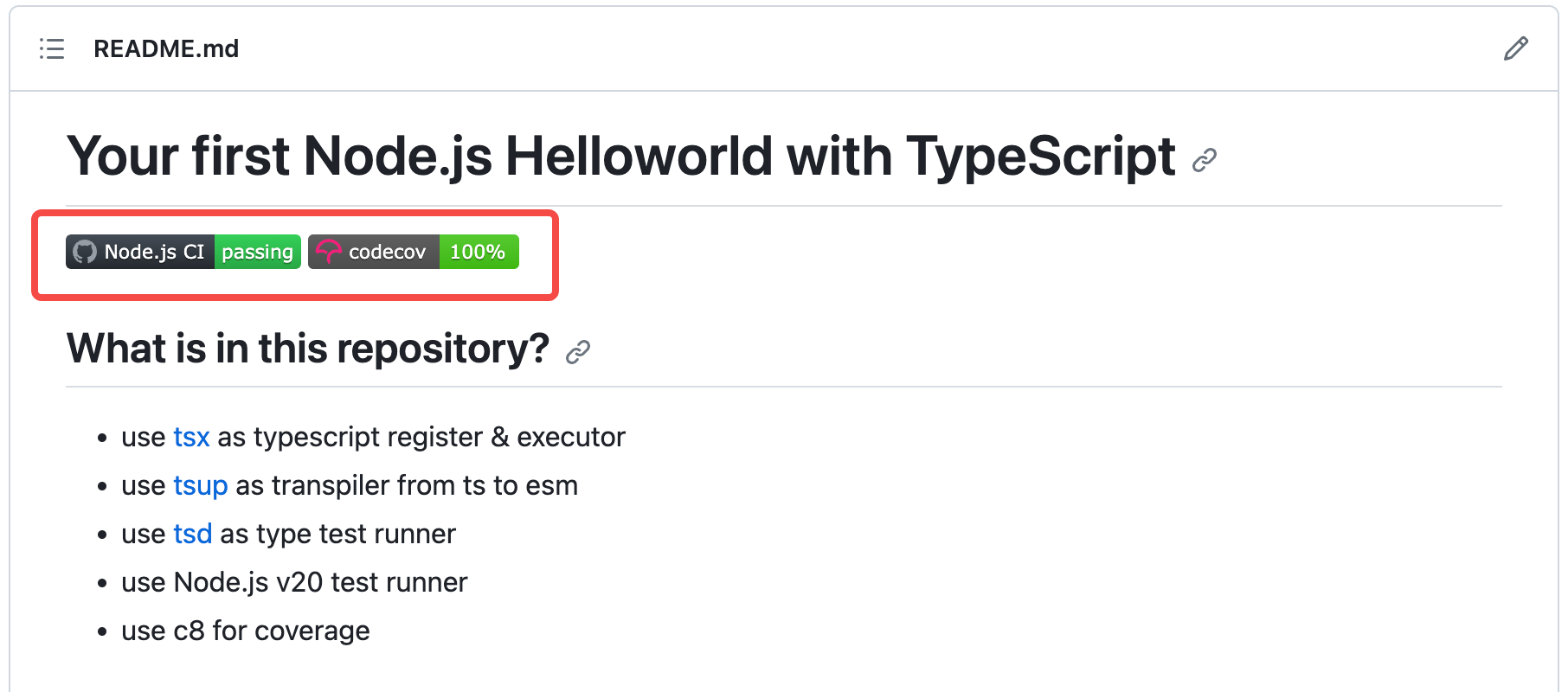
示例1:测试通过
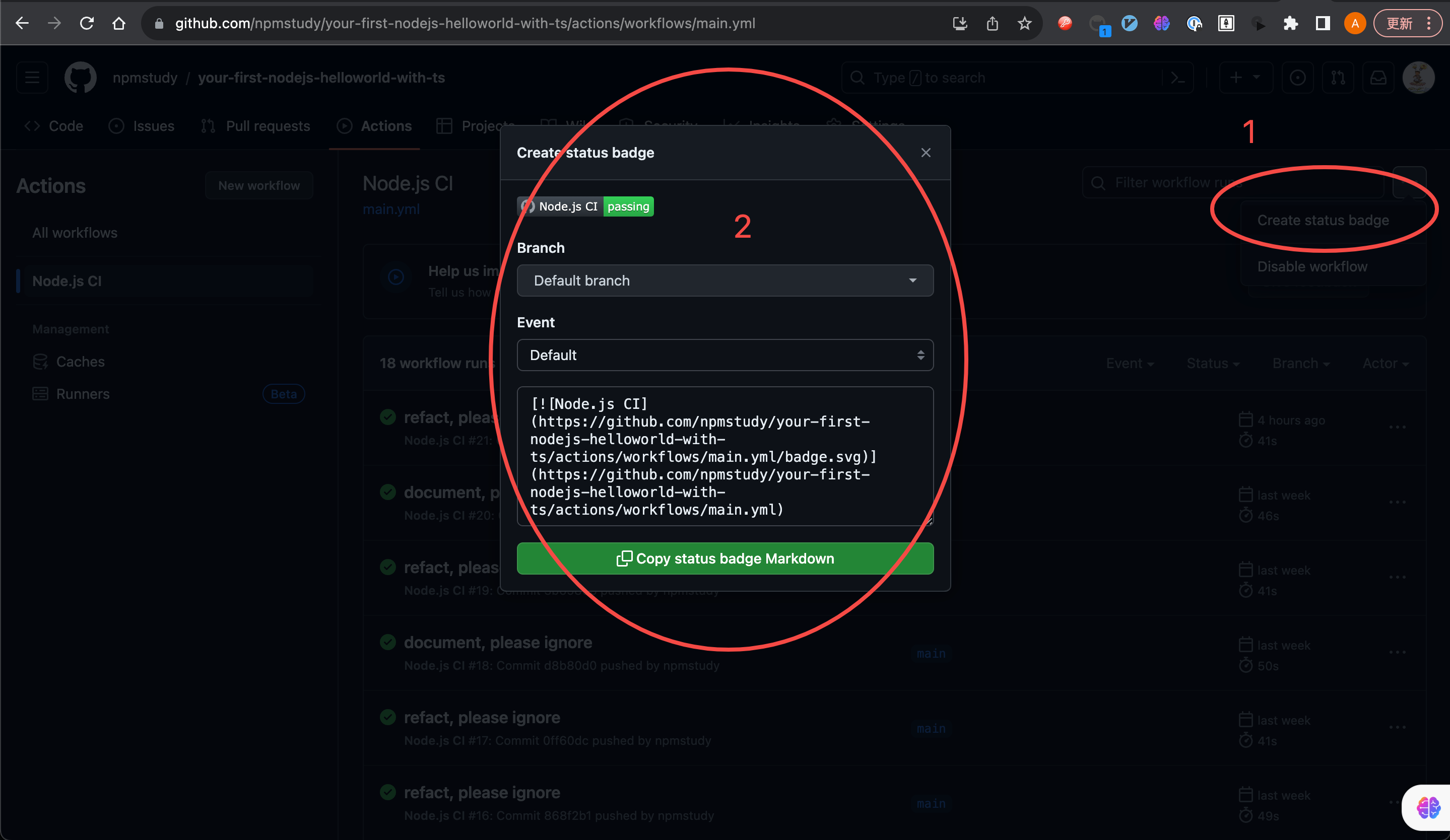

示例1:测试覆盖率
https://glebbahmutov.com/blog/trying-node-test-runner/#code-coverage